Eating once every 24 hours seems like an impossible mission, but many people practice it. OMAD (which stands for “one meal a day”) is a form of intermittent fasting that is believed to help with weight loss.
Of course, not everyone is pursuing weight loss goals; some just want to be healthier or spend less money on food. Whichever group you hang out with, we’ve found a few things that happen to a lot of people after drastically changing their diets.
We explain how your body reacts to this sudden food shortage.
You Might Gain Weight
In cases of food scarcity, your body switches to “starvation mode” and stores all the food you eat, so you have it for later when you need it most.
Basically, it slows down your metabolism. To top it off, it increases the production of cortisol (stress hormone), and this causes you to accumulate fat.
Your Blood Sugar Level Might Become Unstable

Long periods without eating often lead to unstable blood sugar levels. Hypoglycemia (extremely low blood sugar) is usually caused by fasting, especially if you have type 2 diabetes. Later, you may experience muscle tension that leads to headaches.
You Might Lack Nutrients

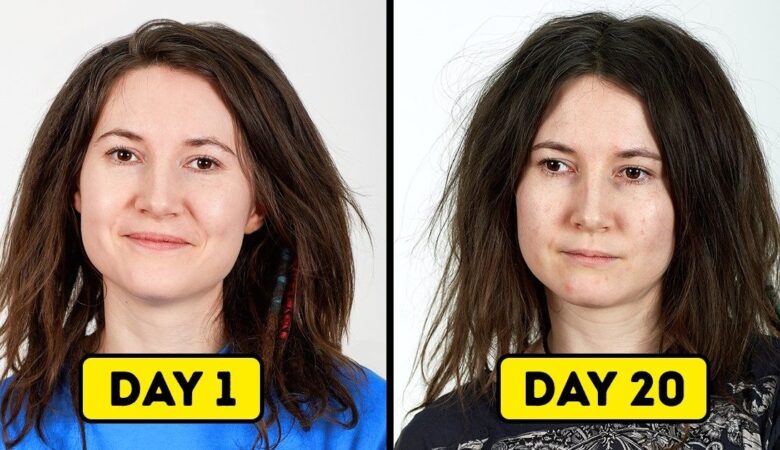
One meal a day may not be able to provide enough vitamins. As a result, you are at a higher risk of developing the ramifications of a vitamin deficiency.
For example, hair loss is often associated with a lack of nutrients. For its part, white spots on the nails (leukonychia) are usually caused by a deficiency of zinc and calcium.
Your Social Life Might Deteriorate
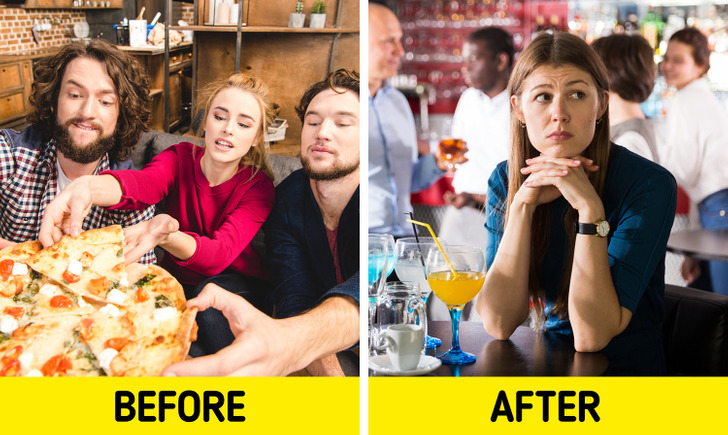

Lunches at work, family gatherings, and birthdays – all of these social events will go unnoticed because you are restricted to one meal.
As a result, your family and friends will preach about the proper diet and inevitably question your common sense. In addition, you will also be more irritable from hunger.
You Might Suffer From Headaches
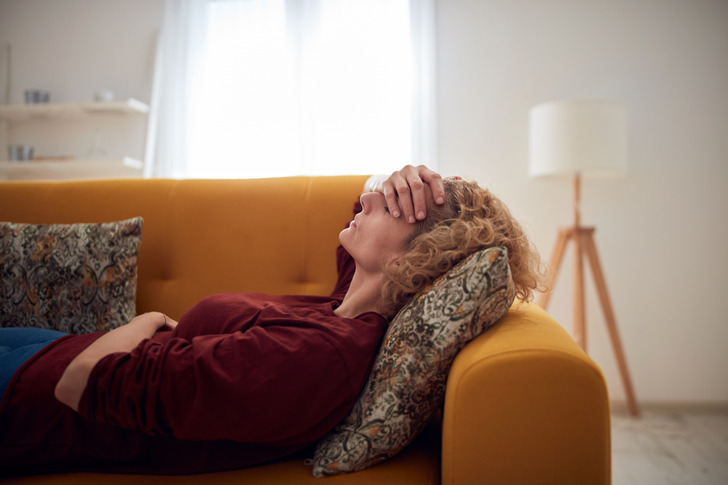

“Diet headaches” are quite common among those who want to lose those extra pounds as quickly as possible. They occur for a variety of reasons, whether due to an adjustment period, drop in blood sugar levels, magnesium deficiencies, and many others.
You Might Always Be Cold
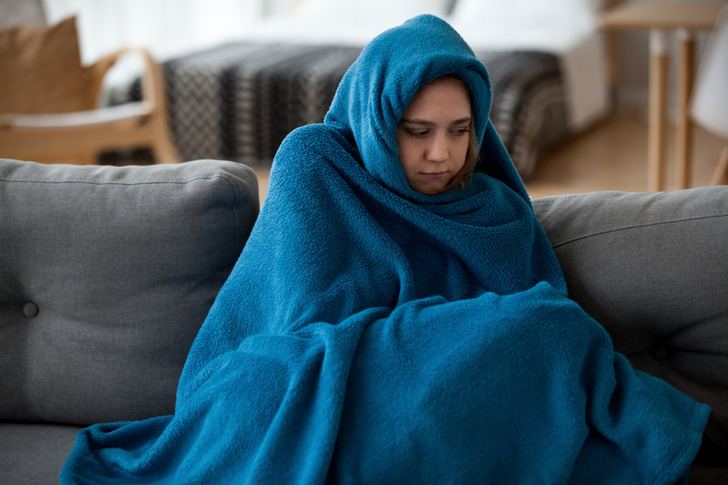

Eating one meal a day diverts blood flow to fat storage. In this form, it stores energy and, in an emergency, gives you strength and agility.
A low amount of calories makes you feel constantly cold and hungry.
What do you think of this approach? How many times a day do you eat?
Preview photo credit Depositphotos.com







Leave a Reply