Dairy products have long been a staple in many diets, offering a rich source of calcium, protein, and vitamin D. However, an increasing number of people are choosing to go dairy-free for various reasons, including concerns about lactose intolerance, acne, or even ethical and environmental considerations. But what exactly happens to your body when you stop eating dairy? In this comprehensive guide, we explore the potential benefits and drawbacks of a dairy-free lifestyle. We’ll examine how cutting dairy might reduce headaches, improve emotional stability, decrease bloating, clear up skin, and also discuss the nutrient gaps you need to be aware of.
What Happens to Your Body If You Stop Eating Dairy
Headache Relief: How Cutting Dairy May Reduce Migraines
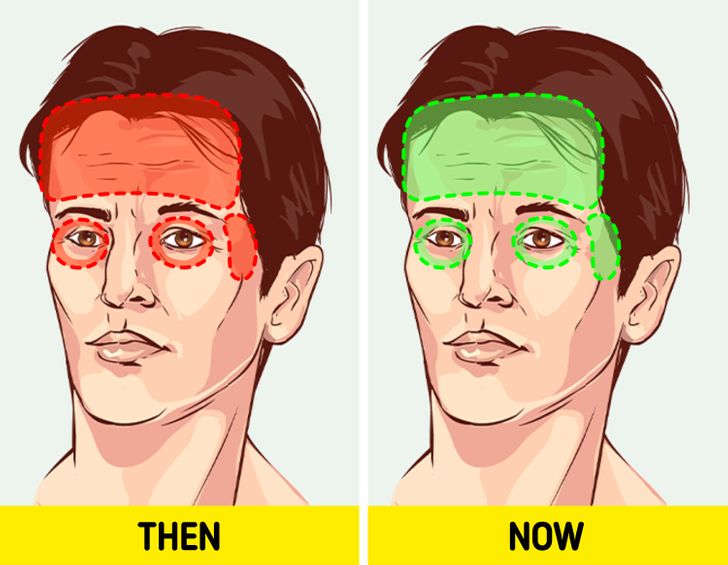
For many, dairy products can be a hidden trigger for headaches and migraines. Certain compounds found in dairy—such as hormones and biogenic amines—may cause inflammation or allergic reactions in susceptible individuals, leading to frequent headaches. Studies have indicated that eliminating dairy from your diet may help reduce the intensity and frequency of migraines.
Research from sources like Mayo Clinic suggests that some individuals who experience chronic headaches may see improvements when they remove potential dietary triggers, including dairy. Furthermore, reducing dairy intake can decrease inflammation in the body, which is a common culprit behind headaches. By choosing dairy alternatives such as almond milk or oat milk, you might experience a significant reduction in headache symptoms, leading to an overall improvement in your quality of life.
Improved Emotional Stability: The Dairy-Free Effect on Mood

A lesser-known benefit of stopping dairy consumption is its potential impact on emotional well-being. Many people report that a dairy-free diet helps stabilize their mood and reduce feelings of anxiety and depression. This could be partly due to the role that inflammation plays in mental health. Dairy products have been linked to increased inflammatory markers in some individuals, which may affect brain function and mood regulation.
For instance, research shared on Harvard Health Publishing highlights that diets high in inflammatory foods can contribute to mood swings and even depressive symptoms. By eliminating dairy, you might reduce systemic inflammation, which in turn can lead to more stable emotions. Moreover, some dairy proteins have been known to trigger allergic reactions that can indirectly impact your mood by causing discomfort or stress. Switching to a dairy-free diet may also encourage the intake of other mood-boosting foods like leafy greens, fruits, and whole grains—nutrient-dense choices that support overall mental health.
Reduced Bloating and Improved Digestion: Benefits of a Dairy-Free Diet
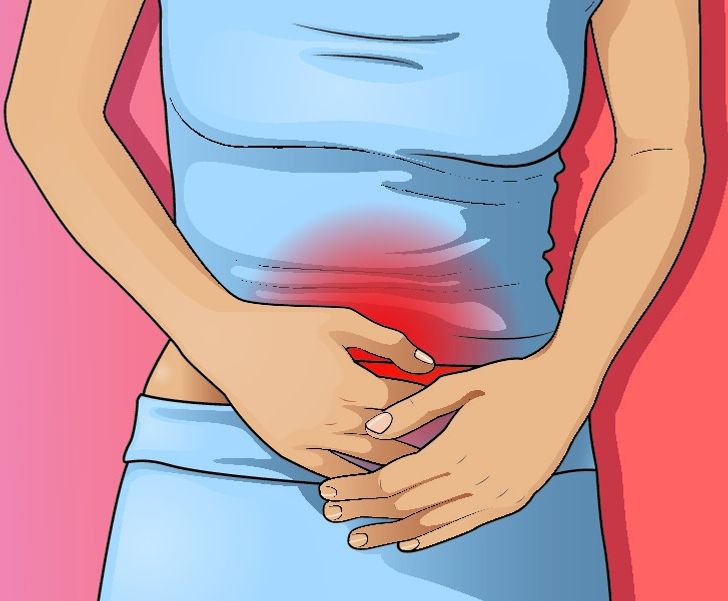
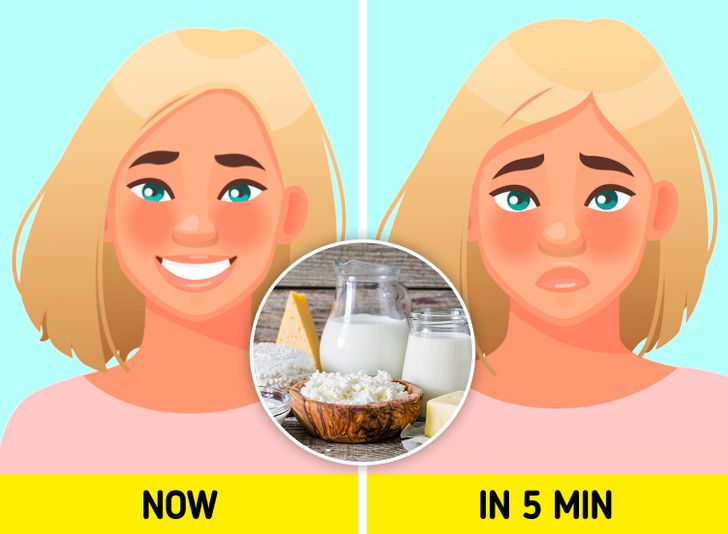
Bloating is a common complaint among dairy consumers, particularly for those with lactose intolerance. Lactose, the sugar found in milk, can be difficult for some people to digest, leading to gas, bloating, and other uncomfortable gastrointestinal symptoms. When you stop eating dairy, your body no longer has to struggle with breaking down lactose, often resulting in reduced bloating and a calmer digestive system.
According to WebMD, many people who are lactose intolerant experience significant relief once they remove dairy from their diet. In addition to alleviating bloating, a dairy-free diet can also help prevent more severe digestive issues such as diarrhea and abdominal cramping. For those suffering from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or other digestive disorders, exploring dairy alternatives may lead to improved gut health and enhanced overall digestion.
Clearer Skin and Acne Reduction: The Impact of Removing Dairy
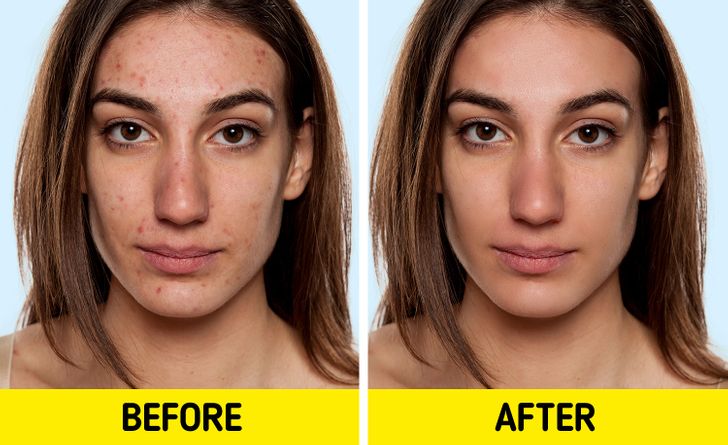

One of the most popular reasons for adopting a dairy-free lifestyle is the potential improvement in skin health. Many individuals who struggle with acne and other skin conditions have found that cutting out dairy leads to clearer, healthier skin. This connection is often attributed to the hormones and bioactive molecules present in milk, which may exacerbate acne and other inflammatory skin conditions.
For example, a study highlighted on Healthline suggests that dairy consumption can increase the production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), a hormone that may contribute to acne development. When you eliminate dairy from your diet, you might see a decrease in IGF-1 levels, leading to reduced inflammation and fewer breakouts. Furthermore, a dairy-free diet often encourages the consumption of more fruits, vegetables, and whole foods that are rich in antioxidants and other skin-friendly nutrients. By choosing alternatives like coconut or soy milk, you not only avoid potential acne triggers but also provide your body with beneficial nutrients that promote clear and vibrant skin.
Nutrient Considerations: Essential Nutrients You Might Miss Out On

While there are several benefits to stopping dairy consumption, it’s important to be aware of the potential nutrient gaps that may arise. Dairy products are a significant source of calcium, vitamin D, and high-quality protein—nutrients that are essential for bone health, muscle function, and overall vitality. When you remove dairy from your diet, you must ensure that these nutrients are obtained from other sources.
For example, calcium can be found in leafy greens like kale and broccoli, fortified plant-based milks, and tofu. Vitamin D, which is crucial for calcium absorption, may require supplementation or increased exposure to sunlight, particularly in regions with limited sunshine. Protein, too, can be sourced from legumes, nuts, and seeds. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) offers comprehensive guidelines on nutrient intake, which can help you plan a balanced dairy-free diet.
It is essential to plan your meals carefully if you decide to go dairy-free. Consulting a nutritionist or dietitian may be beneficial to ensure that you’re not missing out on vital nutrients that could affect your long-term health.
Balancing the Benefits and Drawbacks: Making an Informed Decision
The decision to eliminate dairy from your diet is highly personal and should be based on your unique health needs and lifestyle preferences. On one hand, many people experience noticeable improvements in symptoms like headaches, bloating, and acne after removing dairy. On the other hand, dairy is a rich source of nutrients that support various bodily functions, so it’s critical to replace these nutrients with other food sources or supplements.
Here are some practical tips for transitioning to a dairy-free diet without compromising your nutritional intake:
- Explore Dairy Alternatives: Options such as almond milk, coconut milk, and oat milk can serve as excellent substitutes for traditional dairy. Look for products fortified with calcium and vitamin D to ensure you receive similar nutritional benefits.
- Increase Calcium-Rich Foods: Incorporate plenty of green leafy vegetables, fortified cereals, tofu, and legumes into your diet to maintain strong bones and healthy muscles.
- Consider Vitamin D Supplements: Especially in regions with limited sunlight, a vitamin D supplement can help support calcium absorption and overall health.
- Balance Your Protein Intake: Include high-quality plant-based proteins like quinoa, lentils, and beans to meet your daily protein needs.
- Monitor Your Body’s Response: Keep a food diary to track any changes in your symptoms, whether improvements or new concerns, as you adjust your diet.
For more detailed guidance on transitioning to a dairy-free diet, trusted resources like Harvard Health and WebMD offer expert advice and meal planning tips.
Additional Health Benefits of a Dairy-Free Diet
Beyond the specific areas discussed, a dairy-free diet may have several additional health benefits. Many individuals report increased energy levels, improved digestion, and a reduced risk of certain inflammatory conditions when they cut out dairy. This shift often leads to an overall healthier lifestyle, as it encourages the exploration of diverse, nutrient-dense foods that might otherwise be overlooked.
A dairy-free diet can also contribute to weight loss for some people. Without the added calories and saturated fats found in many dairy products, you may find it easier to manage your weight. Moreover, many dairy alternatives are lower in calories and fat, making them a popular choice for those seeking to shed pounds while still enjoying a rich and varied diet.
Expert Opinions and Research Insights
To further understand the effects of eliminating dairy from your diet, it’s important to look at the opinions of nutrition experts and recent research findings. Numerous studies have explored the relationship between dairy consumption and various health outcomes, providing valuable insights into how a dairy-free lifestyle might impact your body.
For example, research published in journals accessible through PubMed has examined the potential links between dairy intake and conditions like acne, migraines, and gastrointestinal discomfort. While the findings are not always conclusive, many studies support the notion that reducing dairy can alleviate symptoms for individuals with specific sensitivities. By staying informed through reputable sources, you can make educated decisions about your diet and overall health.
Real-Life Experiences: Success Stories and Cautionary Tales
The experiences of those who have embraced a dairy-free lifestyle can be both encouraging and enlightening. Many people share success stories online—describing dramatic reductions in headaches, a clearer complexion, and even improved emotional well-being after cutting out dairy. These testimonials often highlight the importance of listening to your body and adjusting your diet based on your personal health needs.
However, there are also cautionary tales. Some individuals have reported unexpected challenges, such as nutrient deficiencies or difficulty finding satisfying dairy alternatives. Their experiences underscore the importance of careful meal planning and possibly seeking professional dietary advice before making significant changes to your eating habits.
Conclusion: Weighing the Pros and Cons of a Dairy-Free Diet
Deciding to stop eating dairy is a major dietary shift that can yield both impressive benefits and potential challenges. On the positive side, you might experience fewer headaches, a more stable mood, reduced bloating, and clearer skin—all of which contribute to an improved quality of life. On the other hand, dairy is a valuable source of essential nutrients, and eliminating it requires careful planning to avoid deficiencies.
The key takeaway is that a dairy-free diet isn’t inherently good or bad—it’s all about finding what works best for your body. Whether you’re motivated by health concerns, ethical considerations, or simply a desire to try something new, being informed about the changes your body may experience is crucial. Make sure to replace dairy with nutrient-rich alternatives, monitor your health closely, and consult with healthcare professionals if necessary.
For further reading on dairy-free diets and their health implications, consider exploring reputable sources such as Harvard Health, Mayo Clinic, and WebMD. These platforms offer in-depth articles, expert advice, and practical tips that can help you navigate the transition to a dairy-free lifestyle.
Embracing a dairy-free diet may lead to significant improvements in your overall health and well-being, but it’s important to approach the change with a well-rounded understanding of both the benefits and potential risks. By staying informed and making mindful dietary choices, you can harness the positive effects of eliminating dairy while ensuring your body receives all the nutrients it needs for optimal performance.
Preview photo credit Depositphotos.com







Leave a Reply