How Anger and Yelling Impact Your Brain and Body
A 2018 survey revealed that 22% of participants reported feeling angry, while 39% experienced extreme worry. While anger is a natural survival mechanism, it often spirals out of control when stress levels rise, leading to serious health consequences.
Unchecked anger can result in physical and emotional symptoms that often go unnoticed until they worsen. Here’s what happens to your body and mind when you scream, and how you can manage anger effectively.
What Happens to Your Body When You Scream?
Your Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Skyrocket
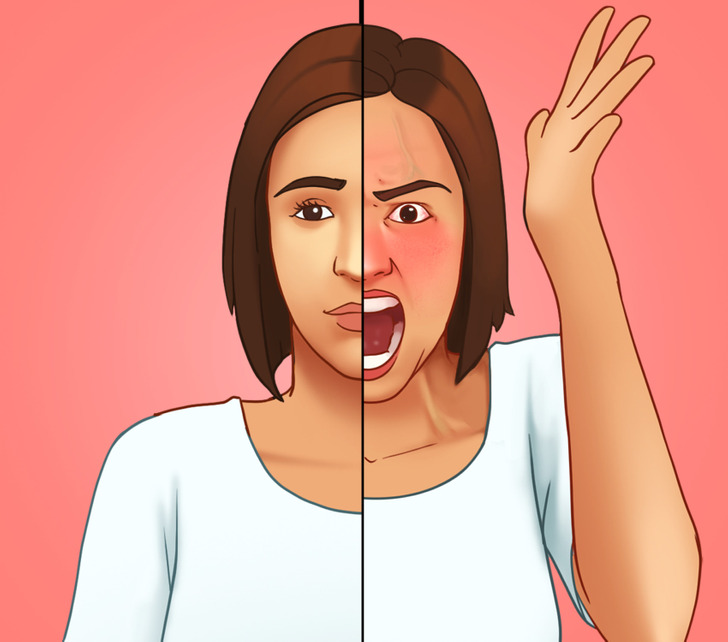

Every time you raise your voice during a heated argument, your heart rate increases significantly, which elevates your blood pressure. This explains the flushed cheeks, protruding veins, and rapid breathing you may notice.
This physical response directs oxygen and nutrients to your major organs, preparing your body for a fight-or-flight response. However, you might also experience cold hands and feet due to reduced blood flow to extremities.
Your Immune System Weakens
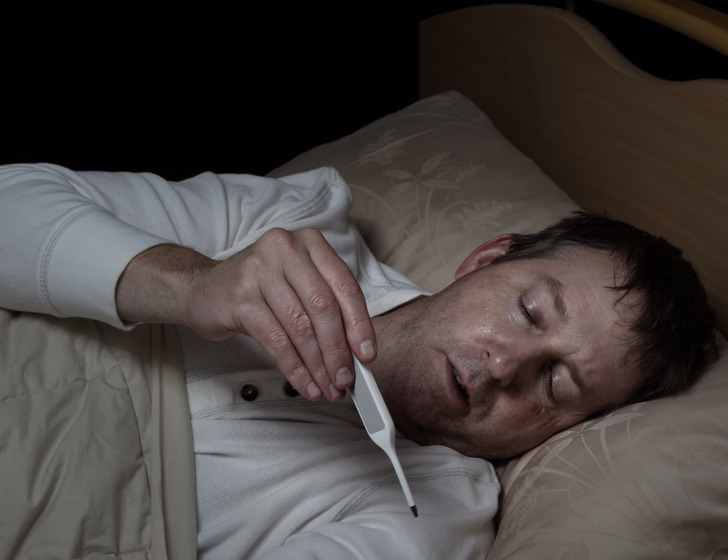

Studies reveal that even recalling a past argument can lower your immune defenses for up to 6 hours. This is especially harmful to those who are usually calm but get angry occasionally.
For people prone to frequent anger, the immune system takes a severe hit, increasing vulnerability to illnesses. The combination of stress and anxiety can leave your health at serious risk over time.
Anger Can Trigger Chronic Health Problems
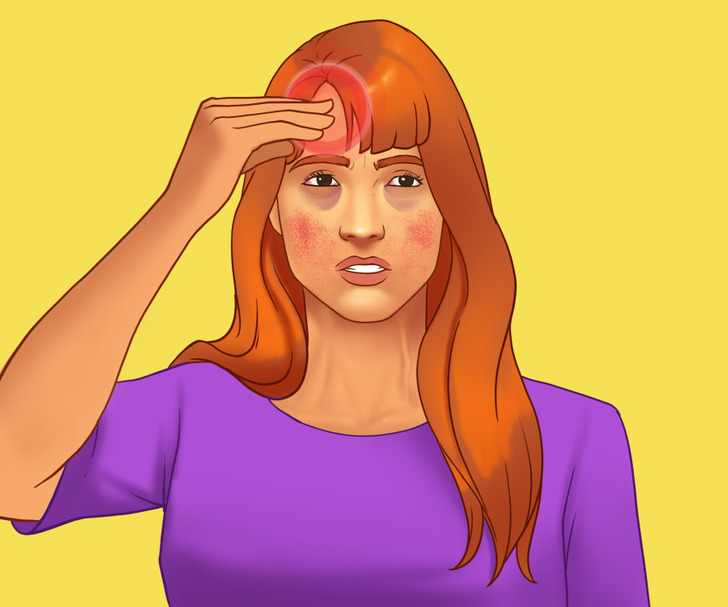

Anger releases stress hormones that alter your metabolism, leading to:
- Headaches
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Digestive problems
In severe cases, anger-related stress can even cause skin conditions like eczema and increase the risk of heart attacks or strokes.
Anger Impacts Your Memory

Stressful arguments can also impair your memory. For example, during an angry verbal exchange, people may misremember or forget details entirely. This phenomenon stems from the brain’s inability to process information properly under intense stress.
Yelling Can Lead to Chronic Pain
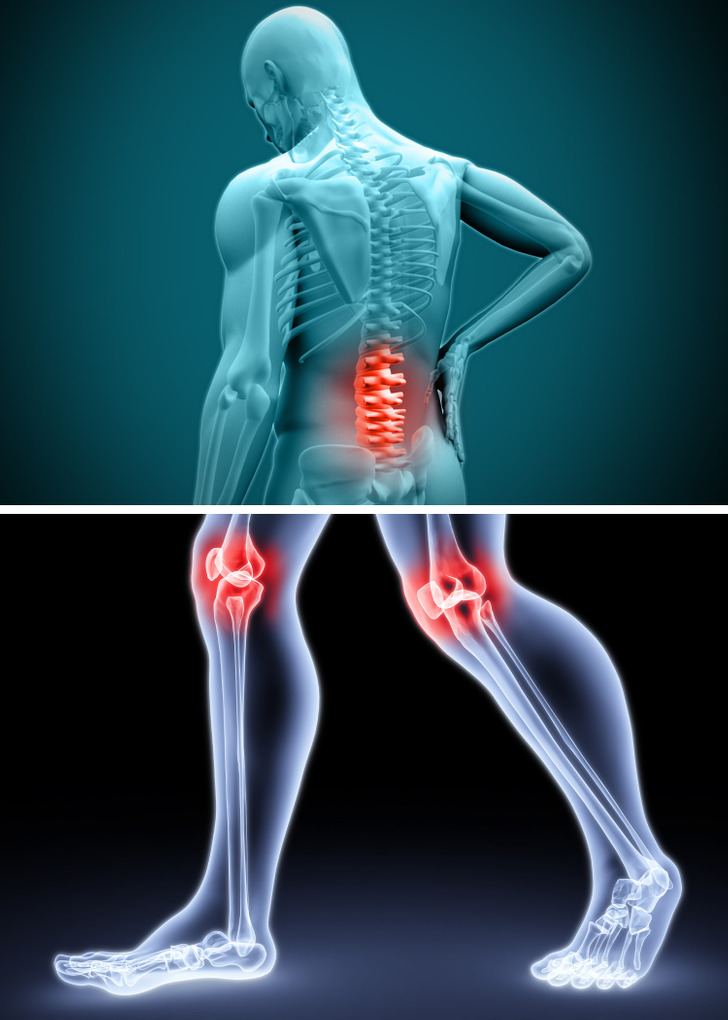
Yelling harms not only the person shouting but also the recipient. This damage can start as early as childhood, leading to:
- Behavioral issues: Children exposed to yelling often exhibit worse behavior as they grow older.
- Altered brain development: Constant yelling impacts the parts of the brain that process sound and language.
- Chronic pain: Long-term effects may include headaches, back pain, neck pain, and even arthritis.
How to Control Anger and Avoid Outbursts
If you find yourself frequently yelling, try these anger management techniques to have healthier conversations:
1. Think Before You Speak
In moments of anger, it’s easy to say something hurtful that you’ll later regret. Take a pause before speaking to avoid causing lasting damage to relationships.
2. Calm Down Before Expressing Frustration
Once you’ve had time to cool off, you can express your concerns in a rational and respectful manner. This approach significantly increases the chances of being heard and understood.
3. Focus on Solutions, Not Problems
Instead of dwelling on the issue, take a break to think of practical solutions. This will help you regain control of your emotions and approach challenges with a clear mind.
4. Let Go of Grudges
Forgiveness is a powerful tool for reducing anger and stress. By letting go of resentment, you free yourself from the negativity that weighs on your mental and physical health.
5. Use Humor to Defuse Tension
Humor (not sarcasm) is an excellent way to handle stress. It allows you to see things from a lighter perspective and manage anger more effectively.
Final Thoughts
Uncontrolled anger can have long-term effects on your physical health, mental well-being, and relationships. By understanding the impact of yelling and adopting effective anger management strategies, you can lead a healthier, happier life.
Do you know other ways to handle anger successfully? Have you dealt with someone whose health suffered due to uncontrolled anger? Share your thoughts in the comments below!







Leave a Reply