Getting a good night’s sleep is crucial for overall health, productivity, and mental well-being. Yet many people struggle with insomnia and restless nights, often without realizing that everyday habits and environmental factors are sabotaging their sleep. In this comprehensive guide, we explore six key reasons why you might be battling sleeplessness and provide actionable solutions to help you achieve the deep, restorative sleep your body craves.
Carpet Allergens in Your Bedroom: How Floor Coverings May Disrupt Your Sleep
Your bedroom should be a sanctuary for rest, but did you know that the very carpet beneath your feet could be a sleep deterrent? Carpets can trap dust mites, pet dander, and other allergens that irritate your respiratory system and trigger sneezing or congestion during the night. For those with allergies or asthma, these allergens can significantly disrupt sleep quality, leading to increased nighttime awakenings and a persistent feeling of fatigue.
Key Points:
- Dust Mites and Allergens: Carpets are notorious for harboring dust mites and allergens, which can exacerbate respiratory issues and contribute to chronic sleep disturbances.
- Cleaning Challenges: Unlike hard floors, carpets require specialized cleaning techniques to remove deeply embedded allergens, making it easier for irritants to build up over time.
- Sleep Quality Impact: The presence of allergens can lead to inflammation and congestion, making it difficult to breathe comfortably and maintain uninterrupted sleep.
For more detailed insights into how allergens affect sleep, refer to resources from the Sleep Foundation.
Inconsistent Sleep Schedule: The Negative Impact of Sleeping In On Weekends

While it might seem tempting to catch up on sleep by sleeping in on weekends, this habit can disrupt your body’s internal clock, or circadian rhythm. A regular sleep schedule is crucial for maintaining optimal sleep quality. Inconsistent sleep patterns can confuse your body’s natural rhythm, leading to difficulties in falling asleep and waking up at consistent times.
Key Points:
- Circadian Rhythm Disruption: Irregular sleep schedules, especially oversleeping on weekends, can lead to a misalignment of your body clock, which in turn affects hormone regulation related to sleep.
- Sleep Debt and Quality: When you sleep in, your body might try to “reset” your rhythm, but this often results in sleep debt and poor-quality rest during the week.
- Long-term Consequences: Over time, irregular sleep patterns can contribute to chronic insomnia, decreased cognitive function, and even mood disorders.
Adopting a consistent bedtime and wake-up routine—even on weekends—can improve sleep quality. For expert advice on maintaining a regular sleep schedule, check out tips from the National Sleep Foundation.
Dairy-Free Diet Concerns: Nutrient Deficiencies Affecting Your Sleep

More people are turning to dairy-free diets for health, ethical, or personal reasons, but eliminating dairy without proper nutritional planning can have unintended consequences on your sleep. Dairy products are rich in calcium and tryptophan, both of which play a role in promoting relaxation and the production of melatonin—the hormone responsible for regulating sleep.
Key Points:
- Calcium and Sleep: Calcium helps the brain use the amino acid tryptophan to manufacture melatonin. A deficiency in calcium can disrupt this process, potentially leading to difficulty in falling and staying asleep.
- Tryptophan and Melatonin: Tryptophan, an essential amino acid found in dairy, is critical for melatonin production. Insufficient levels of this nutrient may impair your ability to get restful sleep.
- Alternative Sources: If you follow a dairy-free diet, consider supplementing with other calcium-rich foods like leafy greens, fortified plant-based milk, or even calcium supplements after consulting with a healthcare provider.
For further nutritional guidance and the impact of diet on sleep, visit Harvard Health Publishing.
Overusing Your Heater: How Indoor Temperature and Humidity Affect Sleep Quality
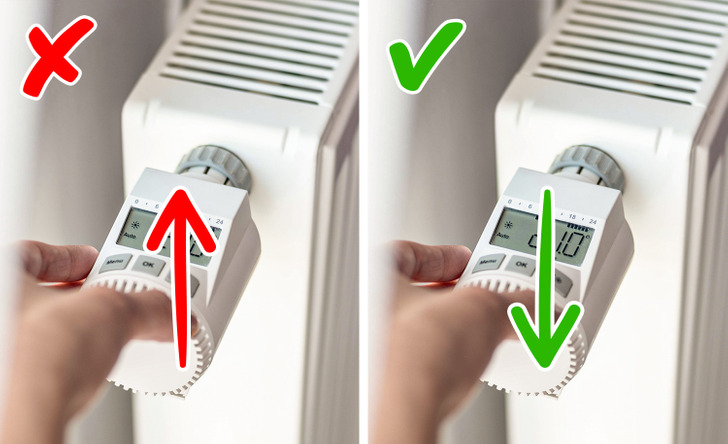

Your bedroom’s climate plays a pivotal role in how well you sleep. While it may be tempting to turn your heater on during cold nights, an overheated room or excessively dry air can actually hinder your sleep quality. Maintaining an optimal sleep environment is essential for deep, uninterrupted rest.
Key Points:
- Optimal Temperature: Sleep experts recommend keeping your bedroom at a cool temperature—usually between 60°F and 67°F (15.6°C to 19.4°C). An overheated room can lead to increased heart rate and restlessness.
- Humidity Levels: Excessive use of heaters can dry out the air, reducing humidity to levels that may cause dry skin, irritated respiratory passages, and discomfort during sleep.
- Air Quality and Ventilation: Overreliance on heaters without proper ventilation can trap indoor pollutants, negatively affecting air quality and contributing to sleep disturbances.
For more detailed guidelines on creating the perfect sleep environment, refer to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and Sleep Foundation.
Late-Night Snacking Habits: The Impact of Eating Before Bed on Sleep

Indulging in late-night snacks might seem harmless, but it can lead to digestive disturbances that impair sleep quality. Eating right before bed can cause acid reflux, indigestion, and a spike in blood sugar levels, all of which can keep you awake or cause frequent awakenings throughout the night.
Key Points:
- Digestive Discomfort: Consuming heavy, fatty, or spicy foods late at night can result in acid reflux and indigestion. These discomforts not only disrupt sleep but can also lead to chronic digestive issues.
- Blood Sugar Fluctuations: Late-night eating can cause rapid changes in blood sugar levels, leading to energy spikes and crashes that affect your ability to fall asleep.
- Sleep Disruption Cycle: The body’s digestive system works best when it’s at rest. Eating before bed forces your body to work on digestion during a time when it should be winding down, further impairing sleep quality.
For more insights on the relationship between diet and sleep, consult resources like WebMD.
Excessive Screen Time: The Impact of Blue Light on Sleep Quality
In today’s digital age, excessive screen time is one of the leading culprits of disrupted sleep. Electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers emit blue light, which can interfere with the natural production of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep. The more time you spend in front of screens before bed, the harder it becomes to fall asleep.
Key Points:
- Blue Light Exposure: Blue light from electronic screens suppresses melatonin production, delaying the onset of sleep and reducing overall sleep quality.
- Digital Detox Benefits: Implementing a digital curfew—such as avoiding screens at least one hour before bed—can help restore your natural sleep cycle.
- Alternative Activities: Engage in relaxing activities such as reading a book, practicing meditation, or listening to calming music to wind down before bed.
For further reading on how blue light impacts sleep, check out information from Harvard Health Publishing.
Practical Strategies to Improve Your Sleep Quality
Now that we’ve explored the six major reasons why you might be struggling to get a good night’s sleep, it’s time to look at practical, actionable strategies to improve your sleep hygiene and overall quality of rest.
1. Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule:
Establish a regular bedtime and wake-up time—even on weekends—to help stabilize your circadian rhythm. Consistency is key to ensuring that your body knows when it’s time to sleep.
2. Optimize Your Bedroom Environment:
Invest in high-quality bedding, adjust the room temperature to a cooler setting, and consider using a humidifier if your room tends to be dry. Removing carpets or regularly deep-cleaning them can also reduce allergen buildup.
3. Be Mindful of Your Diet:
Avoid large meals and heavy snacks close to bedtime. Instead, opt for a light, sleep-friendly snack if you’re hungry before bed. Consider consulting a nutritionist if you’re following a restrictive diet like dairy-free eating to ensure you’re not missing essential sleep-supportive nutrients.
4. Limit Screen Time:
Reduce your exposure to blue light by limiting screen time at least one hour before bed. Use blue light filters on your devices if necessary, and establish a calming pre-sleep routine that doesn’t involve electronics.
5. Practice Relaxation Techniques:
Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help lower stress levels and prepare your body for sleep. Regular physical activity—preferably earlier in the day—can also contribute to a more restful night.
6. Seek Professional Guidance:
If you continue to experience chronic sleep disturbances or insomnia, consider consulting a healthcare professional or sleep specialist. Treatments such as cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) have proven effective for many individuals.
For additional sleep improvement tips and product recommendations, visit reputable sources like the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and Sleep Foundation.
Conclusion: Reclaiming Restful Nights and Revitalizing Your Health
Achieving a good night’s sleep is not an unattainable dream but rather a vital component of a healthy lifestyle that requires careful attention to various aspects of your environment and daily habits. Whether it’s eliminating allergens from your bedroom, sticking to a consistent sleep schedule, rethinking dietary choices, adjusting your indoor climate, avoiding late-night eating, or managing screen time, each small change can collectively transform your sleep quality.
Remember that quality sleep is not only crucial for physical health but also for mental clarity, emotional stability, and overall well-being. By addressing these six common sleep disruptors, you’re taking an active step towards better health and improved productivity. Experiment with these strategies, monitor the changes in your sleep pattern, and make adjustments as needed.
For further guidance on sleep improvement and expert advice, consult trusted resources like Harvard Health Publishing and WebMD. Embrace the journey toward a healthier, well-rested you—because every great day begins with a good night’s sleep.







Leave a Reply