Gluten is called a silent killer because it can cause chronic damage throughout the body. Sometimes, the patient is not even aware of the consequences of gluten consumption.
Craft Side compiled a checklist of gluten sensitivity symptoms.
Gluten Sensitivity Symptoms
1. Problems With The Gastrointestinal Tract

Symptoms are mainly associated with the intestine: nausea, bloating, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and even constipation. People often associate these symptoms with other diseases.
And patients are mistakenly diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Studies confirm that 10-15% of the world population suffers from IBS.
But this diagnosis can lead to people with gluten sensitivity who do not receive adequate treatment so that the symptoms don’t disappear.
2. Unexplained Weight Changes
Gluten intolerance can lead to weight loss and weight gain for no apparent reason. This is due to inflammatory processes at the cellular level and metabolic disorders.
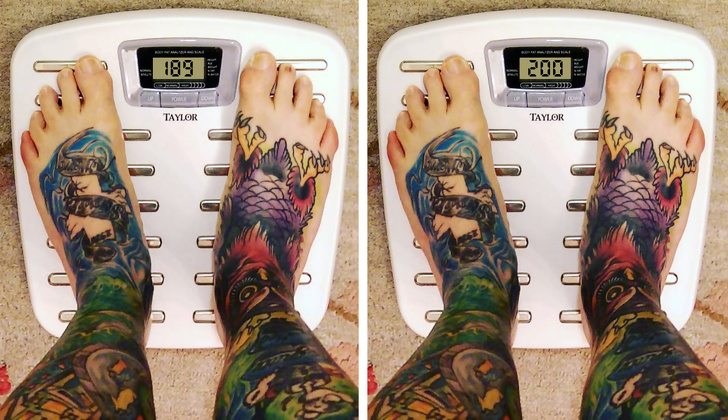
A sudden change in weight can accompany other unpleasant diseases. But it may be related to gluten intolerance if it is accompanied by other symptoms of malabsorption.
3. Hormonal Imbalance

There is a direct relationship between gluten intolerance and hormonal disorders that can occur such as an irregular menstrual cycle, sudden fluctuations in weight, premenstrual syndrome, and sleep disorders.
Hormonal failures caused by gluten intolerance can be amplified many times during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. Remember that these symptoms are mainly recognized among women.
4. Problems With The Central Nervous System

Gluten increases inflammation and permeability of the intestine. As a result, symptoms of gluten sensitivity can include concentration problems, depression, anxiety, insomnia, and fatigue.
Some people with gluten intolerance experience irritability and feelings that they easily lose their line of thinking and have poor concentration.
According to information gathered in a study, people with gluten intolerance are more prone to migraines than other people. The causes of headaches can be very different. A person allergic to gluten can experience a headache 30 to 60 minutes after eating.
5. Skin And Nail Problems
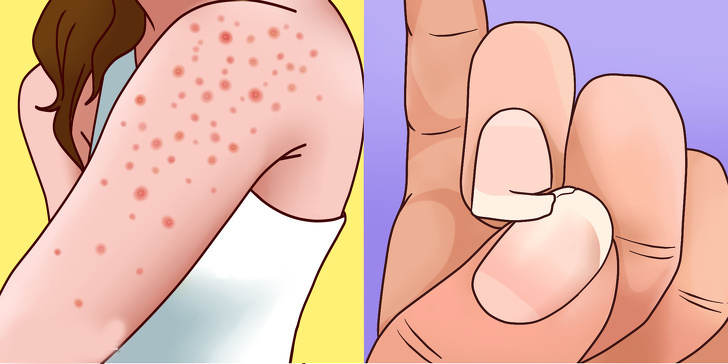
Hair keratosis and herpetiform dermatitis are two skin conditions directly related to gluten intolerance. Symptoms include itching and rashes that may appear on the hands, trunk, face, buttocks, elbows, and hairline.
Another symptom is weakened and brittle nails. Other skin irritations like mimic eczema can signal gluten-induced blockage.
6. ADHD
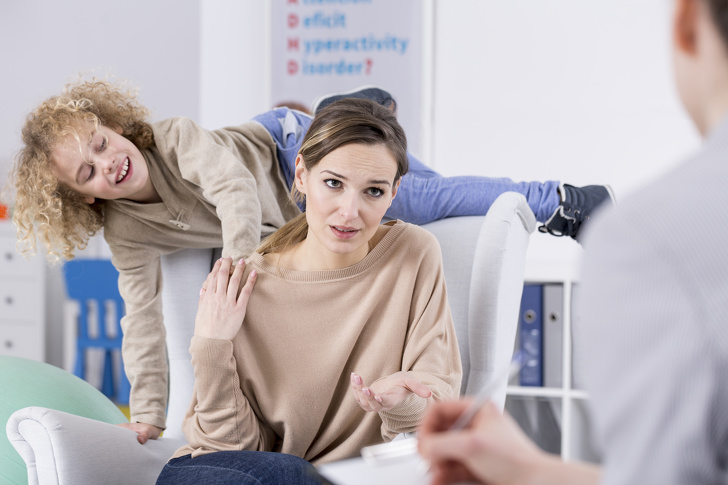

Another disorder that may be associated with gluten intolerance is attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. ADHD can manifest itself in children and adults.
People with this disorder have poor attention span and self-control problems. A gluten-free diet can help reduce the symptoms of ADHD.
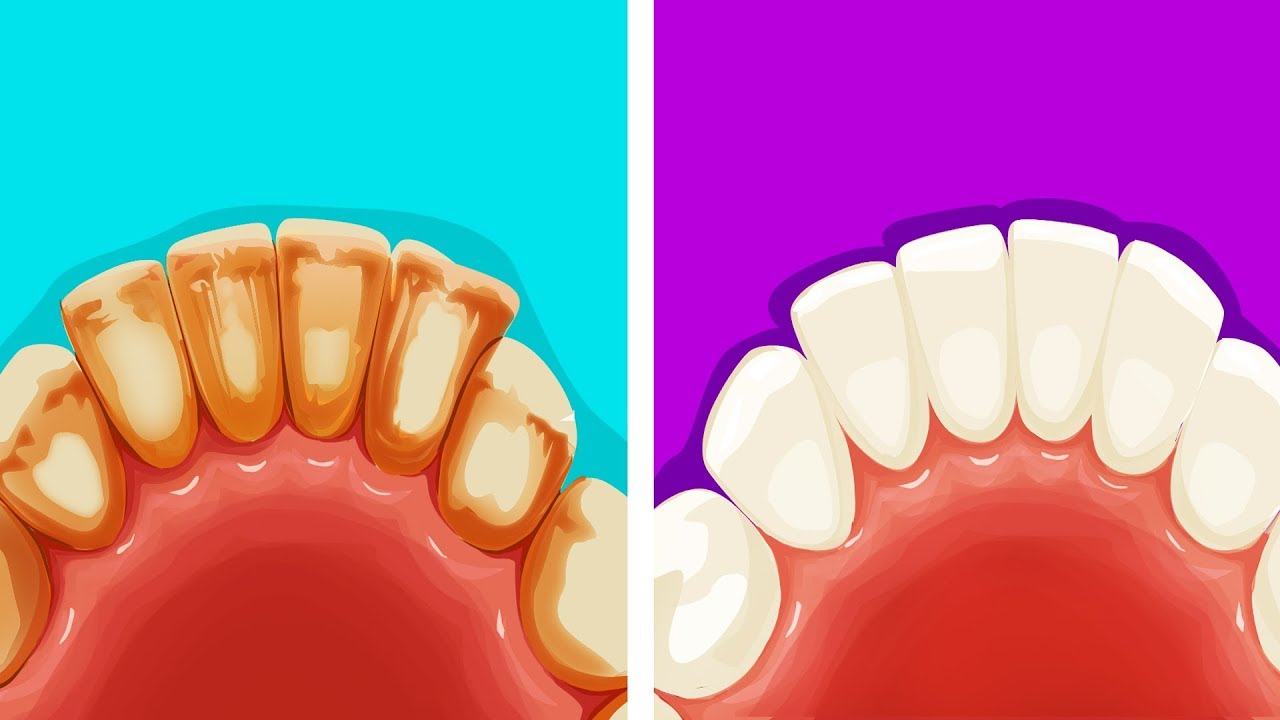
7. Bad Dental Condition
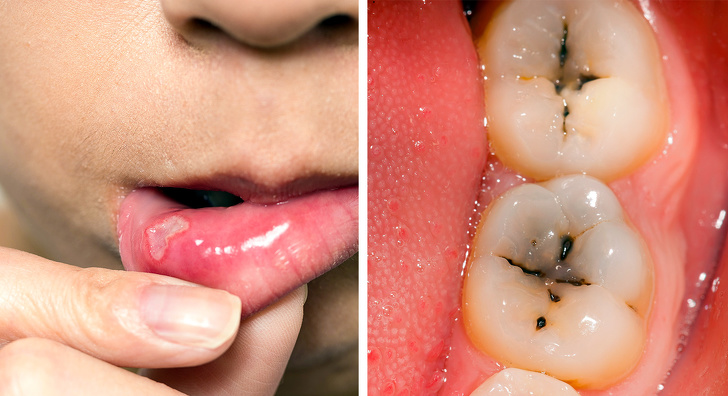
In the case of gluten intolerance, the absorption of the necessary elements and minerals in the intestine is affected. This also applies to calcium. The result can be problems with the teeth and oral cavity: hypersensitivity to enamel, tooth decay, cavities, and mucous ulcers.
If you take good care of your teeth but still notice some problems, the reason may be caused by your gluten consumption.
8. Iron-Deficiency Anemia
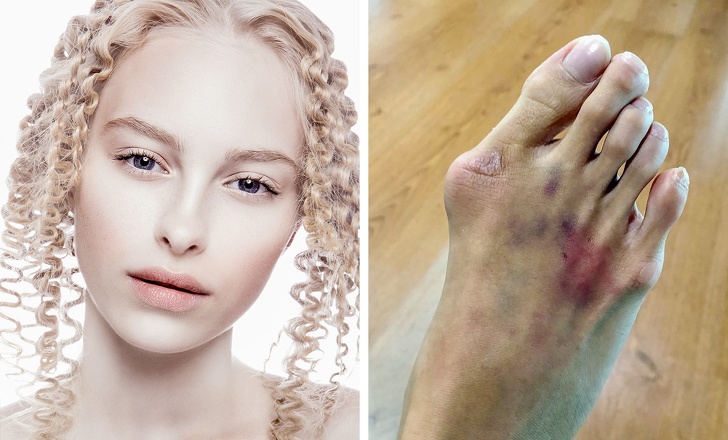
Often, celiac disease is diagnosed due to iron deficiency anemia. Its symptoms include reduced blood volume, fatigue, shortness of breath, headaches, pale skin, mucous membranes, and even arthritis.
Iron is poorly digestible because, with gluten intolerance, there is a deterioration of iron absorption in the intestine.
9. Autoimmune Diseases
Many people with autoimmune diseases have a history of gluten intolerance. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks its own intestinal cells after gluten enters.
The problem is compounded by the fact that this autoimmune disease increases the risk of developing other autoimmune diseases, such as autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune liver disease, Crohn’s disease, diabetes, vitiligo, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
How To Treat Gluten Sensitivity?

Get tested. Your doctor will take a blood sample and look for antibodies that are generally present in the blood of people with celiac disease. Before the examination, you should include gluten in your diet, as this will help avoid inaccurate results.
2. Eliminate gluten from your diet. It’s contained in:
- Wheat
- Rye;
- Bulgur
- Flour
- Semolina;
- And in several other foods.
Always check the composition of the product. Give preference to products that contain the “gluten-free” label.
Have you ever experienced any of these signs of gluten sensitivity? Tell us in the comment.







Leave a Reply